Lesson Four : Star Death
Different types of stars end their lives in different manners. The type of end they come to depends on their original mass as nuclear fusion begins and their remaining mass after nuclear fusion in the core ceases.When stars with an initial mass similar to that of our Sun reach their final stage, the nuclear reactions in their outer shells cease and the star has no remaining energy to resist the inward pull of gravity. As the carbon core collapses into itself and heats up, the outer layers of hydrogen and helium are blown off, forming a beautiful, intricate planetary nebula surrounding the core. The term planetary nebulae is an unfortunate misnomber since these clouds of dust and gas have nothing to do with planets. They are called this because they look like the disc of a planet when viewed through an optical telescope.
Planetary Nebula PN K3-35 in radio
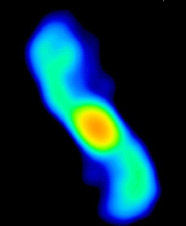
NRAO / AUI

NRAO / AUI
Within the nebula, the core continues to collapse in upon itself. There is a large amount of heat generated by the collapse, but within seventy-five thousand years, the core will cool and the star will become a small white dwarf. Over further billions of years, the white dwarf will completely cool, fade, and become a black dwarf.